2. Conditions that are precancerous
This term refers to benign tumours that
can develop into malignant tumours over time, as is common in anal intraepithelial neoplasia
(AIN) and anal squamous intraepithelial neoplasia (ASIEN) (ASIL).
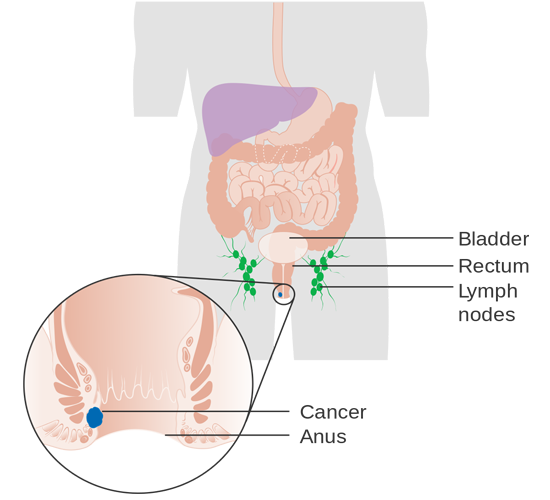
3. Cancer of the squamous cells
These anus malignant tumours are caused by
abnormal squamous cells (cells that line most of the anal canal).
4. Bowen's disease
This condition, also known as squamous cell carcinoma in
situ, is distinguished by abnormal cells on the anal surface that have not invaded deeper
layers.
5. Cancer of the basal cell
Basal cell carcinoma is a type of skin cancer that
commonly affects sun-exposed skin. As a result, it is a very rare form of anal cancer.
6. Adenocarcinoma
This is a rare type of cancer that develops from the glands
that surround the anus.
What factors contribute to anal cancer?
The development of abnormal cells in the body causes anal cancer. These abnormal cells can
proliferate uncontrollably and form masses known as tumours. Cancer cells in advanced stages
can metastasize, or spread to other parts of the body, interfering with normal functions.
Human papillomavirus (HPV) a sexually transmitted infection, is thought to
play a role in the development of anal cancer. It is found in the majority of cases of anal
cancer.
What are the signs and symptoms of Anal Cancer?
Anal cancer symptoms can be confused with haemorrhoids, irritable bowel syndrome
(IBS), and a variety of other gastrointestinal disorders. These are some
examples:
- alterations in bowel habits
- thin stools rectum bleeding pain,
- pressure, or
formation of a lump near the anus discharge from the anus or itching
What are some of the risk factors for anal cancer?
Anal cancer can affect anyone, but some people are more likely to develop it than others. The
following are risk factors:
Infection with HPV
HPV is a group of viruses that are transmitted through sexual contact and remain in the body
after infection. HPV is found in the majority of cases of anal cancer. Prior to the
introduction of routine Pap smears, it was also the leading cause of cervical cancer.
HIV
Because HIV weakens your immune system, you are more likely to develop anal cancer.
Sexual behaviour
Having multiple sex partners and receptive anal sex can raise your risk of anal cancer.
Wearing barrier protection, such as condoms, increases the risk of anal cancer due to an
increased risk of HPV infection.
Smokers
Smokers are more likely to develop anus cancer, even if they quit smoking.
A compromised immune system
A compromised immune system can render your body defenceless in the face of anal cancer. It
is most common in people who have HIV, take immunosuppressants, or have had an organ
transplant.
Advancing years
The majority of cases of anal cancer occur in people over the age of 50.
How is anal cancer identified?
Rectal bleeding is a common symptom of anal cancer. People who experience anus bleeding,
itching, or pain frequently seek medical attention before anal cancer progresses beyond
stage one. Anal cancer is sometimes discovered during routine exams or procedures.
Some cases of anal carcinoma can be detected using digital rectal exams. These are typically
performed as part of a man's prostate exam. Manual rectal exams, in which the doctor inserts
a finger into the anus to feel for lumps or growths, are common in both gender pelvic exams.
Best Hospital for Anal Cancer Treatment in Delhi, Gurgaon.
What is the treatment for anal cancer?
Although there is no cure for anal cancer, many people who are diagnosed with it live healthy
and fulfilling lives. Depending on your age and the stage of your cancer, your doctor may
recommend one of the following treatments, either alone or in combination:
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy can be used to kill cancer cells while also preventing their growth. It can
either be injected or taken orally. Intermittent use of pain relievers may also be necessary
to control symptoms.
Surgery
Local resection surgery is frequently used to remove an anus tumour as well as some healthy
tissue around it. This procedure is most commonly used on patients whose cancer is located
in the lower part of the anus and has not spread to too many nearby structures. It works
best for cancers in their early stages and for small tumours.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy is commonly used to treat many types of cancer, including anus cancer.
X-rays and other forms of radiation are used to kill cancer cells in the body, but they may
also kill healthy tissue nearby. This non-invasive treatment is usually combined with other
cancer treatments.
Anal Cancer Specialist Doctor in Delhi
What is the prognosis for anal cancer?
Many people can live long and healthy lives after being diagnosed with cancer. The key to
long-term health is early detection.
Based on data collected from 2007 to 2013, the overall five-year survival rate for people
with anal cancer is 66.9 percent, according to the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
Furthermore, people with localized anal cancer have an 81.3 percent chance of survival.
Best Anal Cancer Treatment in Delhi, NCR
Anal cancer prevention
There is no sure way to prevent anal cancer, but there are some things you can do to
lower your chances:
Sex should be done safely.
Limiting the number of sexual partners you have, using condoms during sex, avoiding receptive
anal sex, and getting tested for sexually transmitted infections on a regular basis are all
ways to practice safe sex.
Quit smoking.
Stop smoking and try to avoid secondhand smoke as much as possible. If you need assistance,
here are some smoking cessation tips.
Obtain a vaccination
A three-dose series HPV vaccination is approved for both males and females aged 9 to 26. This
vaccine will protect people from certain HPV types that are known to cause anal cancer.
If you have a high risk of anal cancer due to other factors such as family history or age,
talk to your doctor about your concerns.